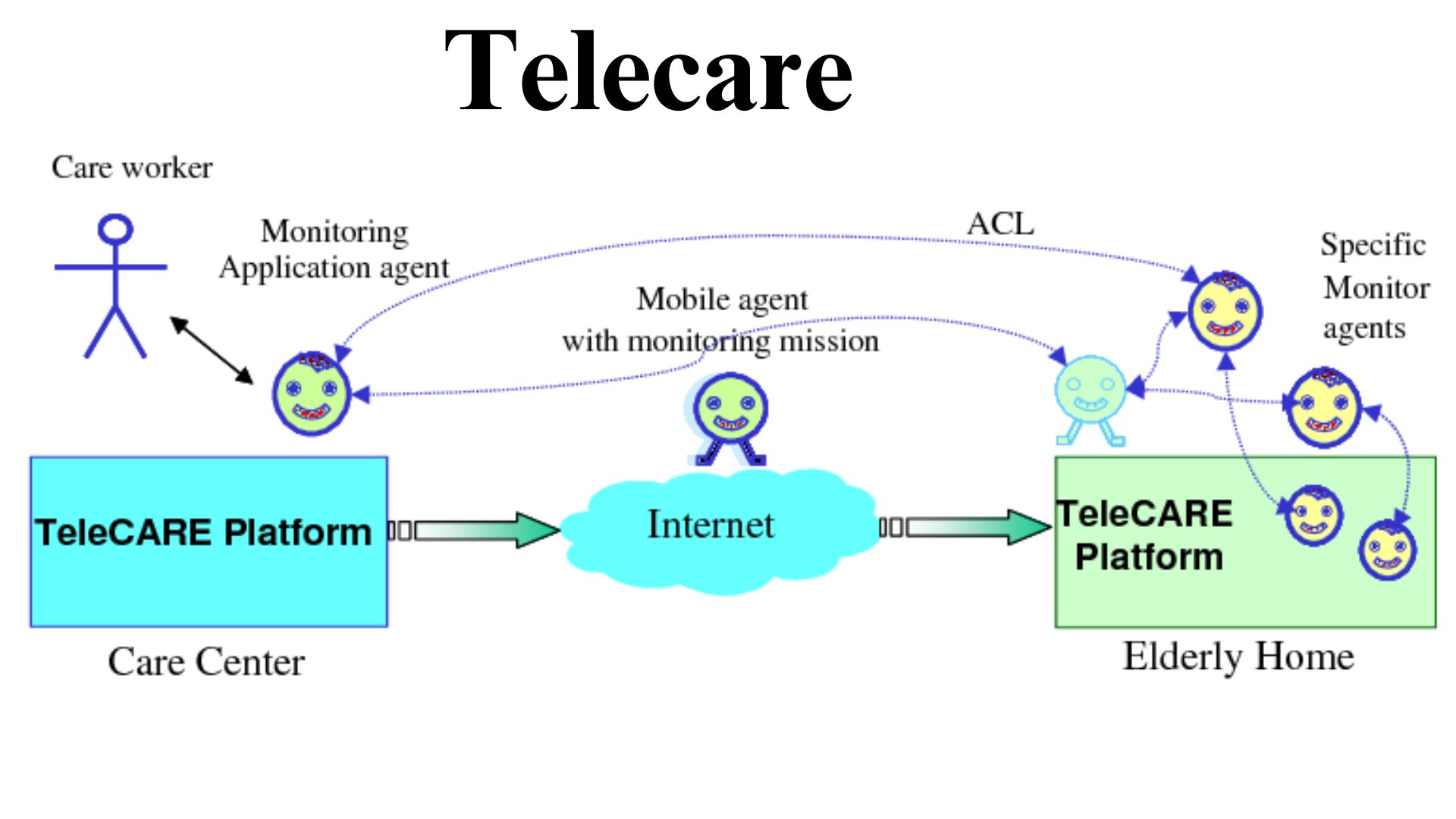
Telecare
Definition and Overview
Telecare represents a subset of telehealth explicitly focusing on providing remote care to patients, primarily the elderly, disabled, and those with long-term health conditions. Its services enable these patients to live independently while ensuring their safety and well-being. By leveraging various communication technologies, its services offer real-time monitoring, emergency response, and routine health checks from the comfort of the patient’s home.
The Evolution of Telecare Services
The concept of telecare has evolved significantly with technological advancements. Initially, it was limited to emergency response systems, known as Personal Emergency Response Systems (PERS), which allowed users to alert healthcare providers or family members during an emergency. Over time, the scope expanded to include medication reminders, fall detection, and health monitoring through wearable devices and home sensors, integrating more sophisticated technologies to provide comprehensive care solutions.
The Role of Technology in Telecare
Technology is the backbone of telecare, enabling the seamless delivery of healthcare services remotely. Innovations such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices, wearable health monitors, smart home technologies, and mobile health applications play a pivotal role. These technologies collect and transmit health data in real-time, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions, intervene proactively, and customize care plans based on the collected data.
The Importance of Telecare
Enhancing Accessibility to Healthcare
Telecare significantly enhances healthcare accessibility, especially for individuals living in rural or underserved areas. It eliminates the need for frequent travel to healthcare facilities, making healthcare services accessible to everyone, regardless of geographical location.
Improving Patient Outcomes
Continuous monitoring and support can lead to earlier detection of health issues, timely interventions, and customized care plans. This proactive approach can improve overall patient outcomes, leading to faster recoveries, better management of chronic conditions, and enhanced quality of life.
Reducing Healthcare Costs
Telecare can potentially reduce healthcare costs by decreasing the need for hospital admissions, shortening hospital stays, and minimizing the need for emergency interventions. Focusing on preventive care and early intervention can lead to significant savings for healthcare systems and patients. Also, Visit my other post, IoT Devices.
How Telecare Works
The Technologies Behind Telecare
Telecare is powered by a wide array of technologies, including but not limited to:
- Wearable Devices: Track vital signs, activity levels, and more, transmitting data to healthcare providers.
- Home Sensors: Detect falls, movements, and unusual behaviour patterns, alerting caregivers or emergency services as needed.
- Communication Platforms: Enable video consultations, remote check-ins, and digital communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- Data Analytics: Analyze health data to identify trends, predict health events, and personalize care plans.
Setting Up Telecare Services
Setting up telecare services typically involves an assessment of the patient’s specific needs, followed by installing necessary equipment and devices in the patient’s home. Training patients and caregivers on using the equipment is crucial for effectively implementing its services.
Examples of Telecare in Action
Telecare represents a significant step in making healthcare more accessible, personalized, and efficient. As technology advances, the scope and effectiveness of its services are expected to expand, further transforming the landscape of healthcare delivery.
- Emergency Response Systems: A senior falls at home and cannot get up. The wearable device detects falls and automatically alerts its service, immediately contacting emergency services and the patient’s family.
- Remote Health Monitoring: A patient with heart disease wears a device that monitors heart rate and blood pressure, transmitting this data to their healthcare provider for daily monitoring. The provider notices an anomaly and contacts the patient for a prompt intervention.
- Virtual Consultations: A patient living in a remote area consults with their doctor via a video call, receiving advice and prescriptions without needing to travel.
Benefits of Telecare
For Patients: Convenience, Comfort, and Continuity of Care
Convenience
Telecare services enable patients to access healthcare from the comfort of their homes. This is particularly beneficial for those living in remote areas, individuals with mobility issues, or those with time constraints that make visiting a healthcare facility challenging. Virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and digital health assessments reduce the need for physical travel, saving time and making healthcare more accessible.
Comfort
Receiving care in a familiar environment can reduce the stress and anxiety associated with medical visits. This aspect can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life for chronic conditions or palliative care, allowing them to stay close to family and in their comfort zone while receiving the necessary medical attention.
Continuity of Care
Telecare facilitates seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring ongoing management of chronic conditions, post-operative care, and long-term therapies. Digital health records and platforms allow for the continuous monitoring of patient health, adjustment of treatment plans in real-time, and easy sharing of information among a patient’s care team, promoting coordinated and comprehensive care.
For Healthcare Providers: Efficiency, Scalability, and Data Utilization
Efficiency
Telecare technologies streamline many processes, from scheduling appointments to managing patient records and monitoring health remotely. This reduces administrative burdens and allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care. Additionally, it can increase the number of patients served, as virtual consultations often take less time than in-person visits.
Scalability
Telecare services can be scaled up to meet increasing demand without needing physical expansion of healthcare facilities. This scalability is crucial in times of health crises, such as pandemics, where there’s a sudden spike in healthcare needs. It also allows for the extension of specialized medical services to underserved areas, bridging the gap in healthcare accessibility.
Data Utilization
Telecare generates vast data that can be analyzed to improve patient care, identify trends, and make informed decisions on public health issues. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can help diagnose diseases, predict outbreaks, and personalize patient care plans based on historical data.

Challenges and Solutions in Telecare
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Telecare relies heavily on technology, which can pose several challenges, including technical glitches, software compatibility issues, and the need for constant updates. Solutions include investing in robust platforms, offering technical support to users, and ensuring systems are user-friendly and compatible with various devices. Regular training for providers and patients on using these technologies effectively can mitigate these challenges.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The digital nature of telecare raises concerns about the privacy and security of patient data. To address these, healthcare providers must adhere to strict data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Implementing advanced security measures, including encryption, secure data storage, and regular security audits, is crucial to protecting patient information.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Resistance from both healthcare providers and patients can hinder the adoption of telecare services. This resistance often stems from unfamiliarity with the technology, concerns about the effectiveness of remote care, and a preference for traditional in-person interactions. Education and awareness campaigns highlighting the benefits of telecare, combined with hands-on training and positive testimonials from early adopters, can help overcome resistance. Additionally, integrating its services to complement rather than replace in-person care can ease the transition for many stakeholders.