Atherosclerosis ICD 10 is a medical condition that occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to a narrowing of the blood vessels. This can restrict blood flow to vital organs, such as the heart and brain, and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) provides a standardized coding system for healthcare providers to diagnose and document atherosclerosis ICD 10 isaccurately.

Coding for atherosclerosis ICD 10 is essential for accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. The coding system allows healthcare providers to document the severity and location of the disease, which can impact treatment decisions and reimbursement. Clinical documentation is also crucial in accurately reflecting the patient’s condition and ensuring appropriate reimbursement from insurance providers.
Key Takeaways:
- Atherosclerosis is a medical condition that occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- ICD10 coding for atherosclerosis provides a standardized system for healthcare providers to accurately diagnose and document atherosclerosis, which is crucial for proper treatment and reimbursement.
- Clinical documentation is essential in accurately reflecting the patient’s condition and ensuring appropriate reimbursement from insurance providers.
Overview of Atherosclerosis ICD 10

Definition and Pathophysiology
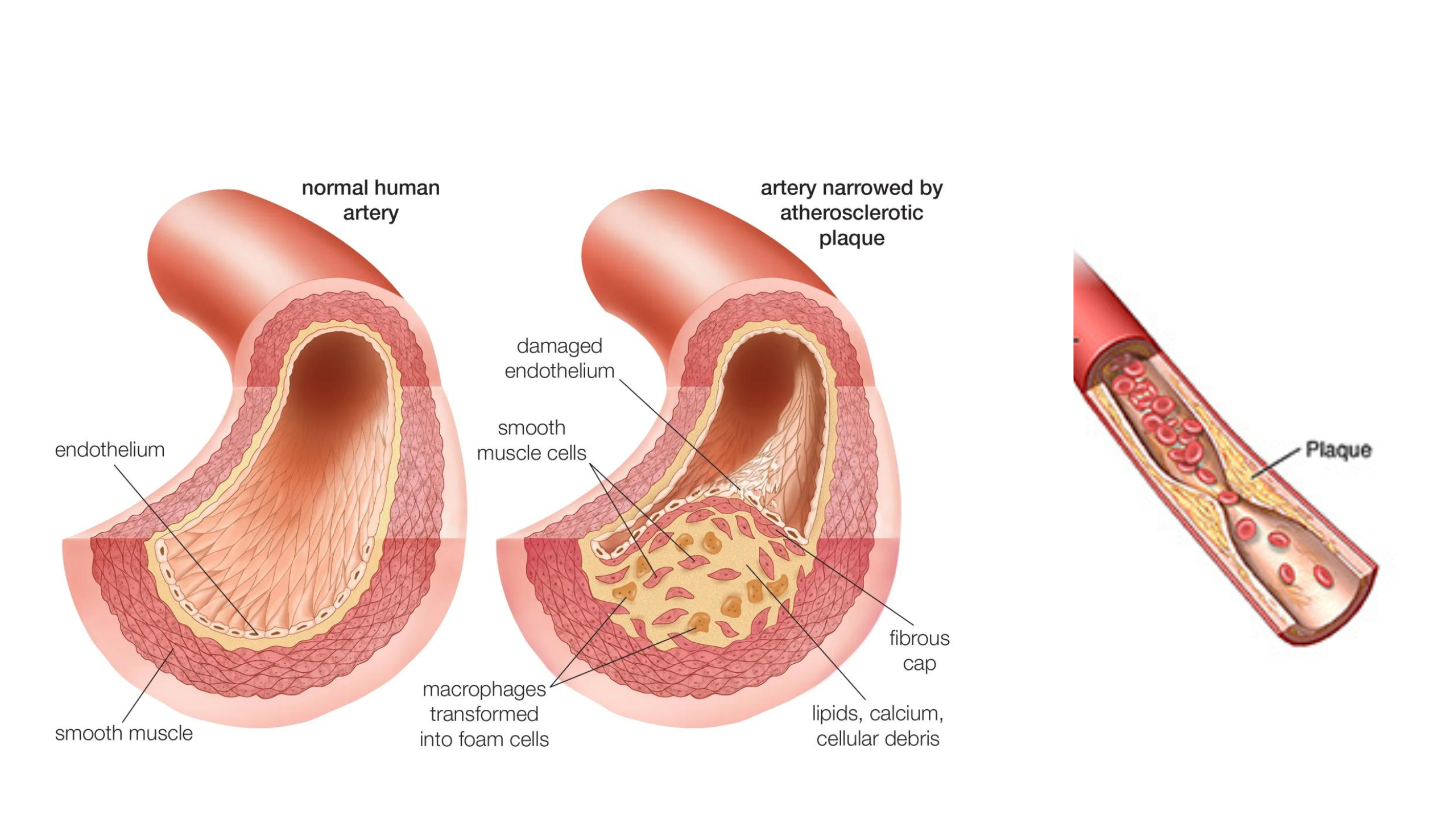
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes plaques to develop on the artery wall. These plaques are made up of cholesterol, fatty substances, calcium, and other cellular debris. As the plaques grow, they can narrow or block the arteries, reducing blood flow to vital organs and tissues.
The pathophysiology of atherosclerosis involves damage to the endothelial cells that line the arterial walls. Various factors, including high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and high levels of LDL cholesterol can cause this damage. When the endothelial cells are damaged, they become more permeable to lipids, allowing them to enter the arterial wall. Once inside the wall, the lipids are taken up by macrophages, which become foam cells and contribute to the formation of the plaque.
Risk Factors of Atherosclerosis ICD 10
There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis ICD 10. These include:
- Age
- Family history of heart disease
- High blood pressure
- High levels of LDL cholesterol
- Low levels of HDL cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stress
Epidemiology
Atherosclerosis is a common disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is the leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for more than 600,000 deaths each year. The incidence of atherosclerosis increases with age, and men are more likely to develop the disease than women. However, after menopause, the risk of atherosclerosis in women increases significantly.
In conclusion, atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the arterial wall, leading to the formation of plaques. There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease, including age, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Atherosclerosis ICD 10 is a common disease that affects millions of people worldwide and is a leading cause of death in the United States.
Coding for Atherosclerosis ICD 10

General Coding Guidelines
Coading for atherosclerosis ICD 10 is based on the guidelines set forth by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The coding guidelines provide detailed instructions on how to assign codes for atherosclerosis and its related conditions.
When coding for atherosclerosis, it is important to follow the coding guidelines and use the most specific code available. Atherosclerosis ICD 10 is should be selected based on the documentation provided by the healthcare provider and should accurately reflect the patient’s condition.
Code Selection Process
The code selection process for atherosclerosis involves identifying the location and severity of the condition. The ICD-10 codes for atherosclerosis are divided into categories based on the location of the affected artery.
For example, atherosclerosis of the coronary artery would be coded using the ICD-10 code I25.1. The specific location and severity of the condition would be further specified using additional codes.
Coding Specificity
Coding specificity is crucial when coding for atherosclerosis. The ICD-10 codes for atherosclerosis are highly specific and require detailed documentation to assign codes accurately.
For example, atherosclerosis of the carotid artery would be coded using the ICD-10 code I65.2. However, if the documentation specifies that the atherosclerosis is bilateral, the code I65.22 should be used instead.
In conclusion, accurate ICD-10 coding for atherosclerosis is essential for proper patient care and reimbursement. Following the coding guidelines and using the most specific codes available is crucial to ensure accurate coding.
Clinical Documentation

Documenting Atherosclerosis
Clinical documentation plays a crucial role in the accurate diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Proper documentation helps healthcare providers understand the severity of the disease, its location, and the extent of the blockage. The ICD-10-CM codes for atherosclerosis are classified under category I70.
When documenting atherosclerosis, it is important to specify the type of vessel affected, such as coronary, cerebral, or peripheral. The documentation should also include the severity of the blockage, whether it is mild, moderate, or severe. Additionally, the documentation should specify the location of the blockage, such as proximal, distal, or bifurcation.
Healthcare providers should use specific and consistent terminology to ensure accurate documentation. They should also document any associated symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or leg pain.
Documenting Complications and Comorbidities
Atherosclerosis can lead to complications and comorbidities, such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. When documenting these conditions, healthcare providers should use the appropriate ICD-10-CM codes that correspond to the specific complication or comorbidity.
It is important to document any other conditions that may be present, such as hypertension, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia. These conditions can exacerbate the effects of atherosclerosis and increase the risk of complications.
In addition to documenting the complications and comorbidities, healthcare providers should also document the severity of the condition and any associated symptoms. This information is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan for the patient.
Overall, proper clinical documentation of atherosclerosis and its associated complications and comorbidities is essential in ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment. By using specific and consistent terminology and documenting all relevant information, healthcare providers can provide the best possible care for their patients.
Treatment and Management of Atherosclerosis ICD 10

Medical Therapies
Medical therapies for atherosclerosis focus on reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke by controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. These therapies may include:
- Lifestyle changes: Patients may be advised to change their diet, exercise routine, and smoking habits to reduce their risk of developing atherosclerosis.
- Medications: Patients may be prescribed medications such as statins, blood pressure-lowering drugs, and antiplatelet agents to control risk factors and prevent blood clots.
- Procedures: Patients with severe atherosclerosis may undergo procedures such as angioplasty or stenting to open blocked arteries.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat atherosclerosis. These interventions may include:
- Endarterectomy: This procedure involves removing the plaque from the inner lining of the affected artery.
- Bypass surgery: This procedure involves creating a new route for blood flow around the blocked artery.
- Atherectomy: This procedure involves removing the plaque from the artery using a catheter-based device.
Patients with atherosclerosis need to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and risk factors. With proper management, many patients are able to control their symptoms and reduce their risk of complications.
Prevention and Education of Atherosclerosis ICD 10
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can prevent atherosclerosis. Patients should be advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains yet low in saturated and trans fats is suggested. Patients should be encouraged to engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week.
Patient Counseling
Patient counseling is an essential component of preventing atherosclerosis. Healthcare providers should educate patients on the risk factors for atherosclerosis, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity. Patients should be advised to monitor their blood pressure and cholesterol levels regularly and to seek medical attention if they have any concerns.
Patients should also be counseled on the importance of medication adherence. Patients with atherosclerosis may require medication to manage their blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Emphasizing the importance of taking medications as prescribed to prevent complications is essential.
In conclusion, preventing atherosclerosis requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and patient counseling. Healthcare providers should work with their patients to develop individualized plans to prevent atherosclerosis and manage any underlying risk factors.
Reimbursement and Billing
Billing Procedures
The billing procedures for atherosclerosis ICD 10 codes are straightforward. The healthcare provider must submit a claim form, which includes the appropriate ICD-10 code for atherosclerosis. The claim form should also include the patient’s insurance information and any other relevant details. It is important to ensure that the claim form is accurate and complete to avoid any delays or denials in reimbursement.
Reimbursement Challenges
Reimbursement for atherosclerosis ICD 10 codes can be challenging due to several factors. One of the primary challenges is the complexity of the disease, which can make it difficult to code and bill accurately. Additionally, insurance companies may have different policies and guidelines for reimbursement, which can vary from state to state. This can lead to confusion and delays in reimbursement.
Another challenge is the increasing emphasis on value-based care, which focuses on quality outcomes and cost-effectiveness. This can lead to tighter restrictions on reimbursement for certain procedures and treatments, including those related to atherosclerosis. Healthcare providers must be aware of these changes and adapt their billing practices accordingly.
In conclusion, healthcare providers must be diligent in their billing procedures and stay up-to-date on the latest reimbursement policies and guidelines to ensure timely and accurate reimbursement for atherosclerosis ICD 10 codes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, atherosclerosis is a serious medical condition that affects a large number of people worldwide. The ICD-10 coding system provides a standardized way to classify and code this disease, which is important for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The use of ICD-10 codes allows healthcare professionals to accurately document and track the prevalence of atherosclerosis, which can help inform public health policies and interventions.
It is important to note that atherosclerosis is a complex disease with many contributing factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Therefore, a comprehensive approach to prevention and treatment is necessary.
Overall, a better understanding of atherosclerosis ICD 10 coding can lead to improved diagnosis, treatment, and, ultimately, better patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ICD-10 code for atherosclerosis of the aorta?
The ICD-10 code for atherosclerosis of the aorta is I70.0. This code is used to indicate the presence of atherosclerosis in the aorta, which is the largest artery in the body.
How is coronary artery disease classified in ICD-10?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is classified in ICD-10 under the code I25. This code indicates the presence of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart.
What is the code for carotid atherosclerosis ICD10 in the ICD system?
The code for carotid atherosclerosis in the ICD-10 system is I65.2. This code indicates the presence of atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain.
How do you specify cerebral atherosclerosis using ICD-10?
Cerebral atherosclerosis is specified using the code I67.2 in the ICD-10 system. This code indicates the presence of atherosclerosis in the cerebral arteries, which supply blood to the brain.
What ICD-10 code is used for general atherosclerotic vascular disease?
The ICD-10 code for general atherosclerotic vascular disease is I70.2. This code indicates the presence of atherosclerosis in any artery in the body except the coronary and cerebral arteries.
How is atherosclerosis of the iliac artery coded in ICD-10?
ICD-10 codes atherosclerosis of the iliac artery under the code I70.2. This code indicates the presence of atherosclerosis in any artery in the body, including the iliac artery, which supplies blood to the legs.
1 thought on “Atherosclerosis ICD 10 Comprehensive Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines”