Outcomes of Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery For Patients Age 80 and Open Heart Surgery
Overview of Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is a complex procedure that involves operating on the heart’s muscles, valves, or arteries. It is commonly used to treat various heart conditions, such as coronary heart disease, congenital heart defects, and valvular heart disease. The surgery requires opening the chest to access the heart and involves a team of specialists and a heart-lung machine. This type of surgery is performed to correct several heart-related problems, including but not limited to, coronary heart disease, congenital heart defects, and valvular heart disease. It’s called “open” heart surgery because it involves opening the chest to expose the heart, allowing surgeons to operate directly on it.
Importance of Understanding Survival Rates
Understanding the survival rates of open heart surgery is crucial for patients and their families as it provides a realistic expectation of the procedure’s outcome. Survival rates offer insight into the surgery’s effectiveness, help assess the risks involved, and assist patients in making informed decisions about undergoing the procedure. These statistics also reflect the advancements in surgical techniques and post-operative care, contributing to improved patient outcomes over the years. Furthermore, survival rates can be a source of hope and reassurance for those facing the prospect of surgery, highlighting the potential for a successful recovery and a return to a healthier life.
What is Open Heart Surgery?
Definition and Types
Open heart surgery refers to any surgical procedure where the chest is opened, and surgery is performed on the heart’s interior structures. It differs from minimally invasive heart surgery, where small incisions and specialized instruments are used, avoiding the need to open the chest fully. The types of open heart surgery vary based on the condition being treated and include:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): CABG is the most common type of adult heart surgery. It improves blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked coronary arteries using blood vessels from other body parts.
- Heart Valve Repair or Replacement: This involves repairing or replacing heart valves that don’t open or close properly.
- Heart Transplant: Replacing a diseased heart association with a healthy heart from a deceased donor.
- Surgery to Repair Aneurysms: Involves repairing or removing aneurysms in the heart or major arteries.
- Surgery for Congenital Heart Defects: Corrects heart defects present at birth.
Common Reasons for Surgery
Coronary artery bypass surgery and open heart surgery are performed to treat a variety of heart conditions, often when other treatments have been exhausted or are deemed ineffective. Common reasons include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the leading cause of surgery. It occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle become blocked.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Involves malfunctioning heart valves that control blood flow through the heart.
- Heart Failure: Advanced stages of heart failure may require surgical intervention to improve the heart’s function.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Birth defects that affect the heart’s normal function and may require surgery for correction.
- Aortic Aneurysm: The enlargement of the aorta, the main artery leaving the heart, can be life-threatening if not treated.
Open heart surgery represents a significant advancement in medicine, offering hope and an improved quality of life for many patients with heart disease. patients undergoing and their families must understand the types and reasons for surgery so that they can make informed decisions about their healthcare options.
Understanding Survival Rates
Explanation of Survival Rate Statistics
Survival rates are critical metrics used in healthcare to gauge the outcomes of various treatments, including open heart surgery. These rates often indicate the percentage of patients who survive a specific period after surgery, commonly one, five, or ten years. Survival statistics help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions by providing a snapshot of the expected outcomes based on historical data. However, interpreting these rates requires an understanding that they are influenced by many risk factors, including the type of surgery, the patient’s age, overall health, and advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques.
Factors Affecting Survival Rates
Several key factors influence survival rates for open heart surgery:
- Patient’s Age and General Health: Older people with multiple health issues may face higher risks during and after surgery.
- Type of Surgery: The complexity and specific nature of the heart surgery significantly impact survival rates.
- Technological and Surgical Advancements: Improvements in medical technology and surgical methods have steadily increased survival rates over time.
- Post-Surgical Care: Effective post-operative care, including follow-up visits and rehabilitation, is crucial for a patient’s recovery and long-term survival.
Recent Advances in Open Heart Surgery
Technological Advancements
In the last 70 years, significant technological innovations have enhanced the safety and effectiveness of open heart surgeries. These include the development of more pubmed heart-lung machines, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and robotics in the operating room. Enhanced imaging technologies now give surgeons better heart visuals, allowing for more precise interventions.
Improvements in Surgical Techniques
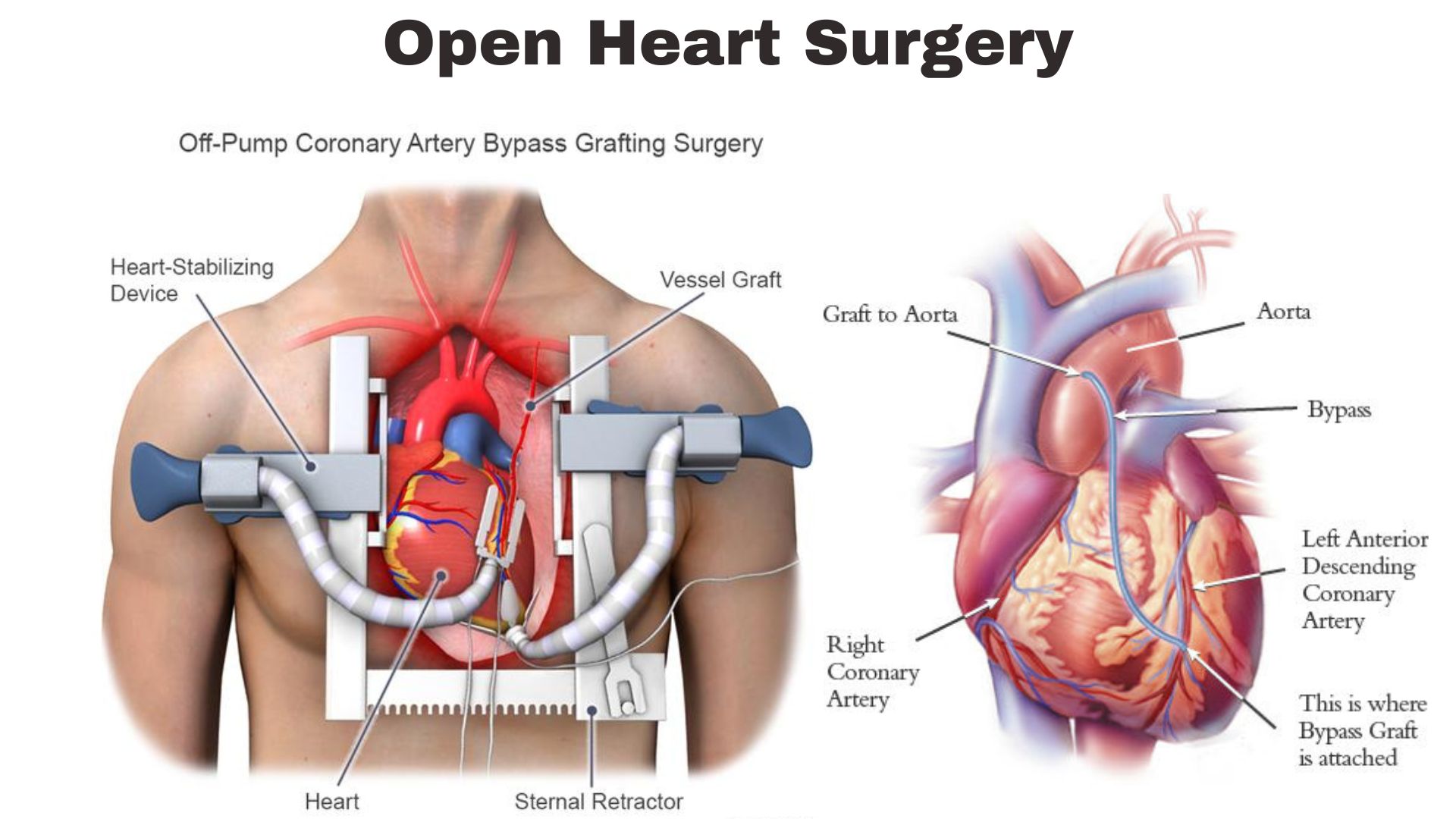
Surgical techniques for open heart surgery have also been considerably refined. For example, off-pump coronary artery bypass (OPCAB) surgery eliminates the need for a heart-lung machine, reducing complications associated with this equipment. Minimally invasive procedures, which involve smaller incisions and less trauma to the body, have contributed to faster recovery times and reduced risk of infections.
Survival Rates by Type of Open Heart Surgery
Survival rates for open heart surgery vary depending on the type of procedure, but recent advancements have contributed to improved outcomes across the board.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Undergoing coronary artery bypass graft is one of the most common types of heart surgery. It is designed to bypass blocked coronary arteries and improve blood flow to the heart muscle. Due to technological and procedural advancements, the survival rate for CABG has significantly improved, with most studies indicating a high one-year survival rate exceeding 90%.
Heart Valve Repair or Replacement
Valve repair and replacement surgeries are performed to address heart valve diseases. With the introduction of more durable prosthetic valves and refined surgical techniques, including minimally invasive approaches, patients now experience better outcomes and longer survival rates. The five-year survival rate post-surgery can vary widely based on age, valve type, and underlying health conditions but generally falls between 70% and 95% for most patients.
Transmyocardial Laser Revascularization (TMR)
TMR is a less common procedure used to treat severe angina when other treatments have failed. It involves using lasers to create channels in the heart muscle, improving blood flow. While TMR is often used as a last resort, advancements in laser technology have made it a safer option with moderate success in reducing angina symptoms and improving quality of life.
Congenital Heart Defect Correction
Surgical correction for congenital heart defects has significantly improved survival rates, especially in pediatric patients. Advances in preoperative care, surgical techniques, and postoperative management have dramatically increased survival rates, with many centers reporting over 90% survival for even complex congenital heart surgeries.
Factors Influencing Survival Rates
Patient Age and General Health
Patient age groups and overall health significantly influence the outcome of open heart surgery. Younger patients with fewer pre-existing conditions generally have higher survival rates due to their body’s stronger resilience and recovery ability. Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity can complicate surgery and recovery, making the management of these conditions critical before surgery.
Type and Complexity of the Surgery
The specific type of open heart surgery and its complexity also play crucial roles in patient survival rates. Surgeries that are more invasive or address more critical parts of the heart, such as valve replacements or repairs and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), can carry higher risks. The surgeon’s expertise and the quality of the healthcare facility are vital factors that can influence the surgery’s success.
Post-Surgery Care and Rehabilitation
Effective post-surgery care, including close monitoring for complications, medication management, and follow-up visits, is essential for a successful recovery. Rehabilitation programs focusing on gradually increasing physical activity, monitoring heart health, and patient education on lifestyle adjustments significantly improve survival rates. Also, please visit my other post, Electronic Health Record (EHR) System.
Improving Your Survival Rates
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Optimal pre-surgery preparation can enhance the chances of a successful outcome. This includes managing existing health conditions, quitting smoking, improving diet, and, if possible, increasing physical fitness levels. Psychological preparation is also important, as a positive outlook can improve the surgical experience and recovery.
Importance of Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care is critical to monitor the patient’s recovery and respond to complications early. Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to assess the heart’s function, the healing of surgical sites, and the effectiveness of medications, adjusting treatments as necessary. Engaging in a structured follow-up program can significantly reduce the risk of post-surgery complications.
Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is one of the most effective ways to improve survival rates after open heart surgery. This includes eating a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. Such changes not only aid in recovery but also contribute to the long-term health of the heart.
Patient Stories and Experiences
Success Stories
The realm of open heart surgery is filled with inspirational tales of resilience, hope, and remarkable recoveries. One such story is of Alex, a 45-year-old who underwent a complex coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Facing a daunting recovery period, Alex adopted a proactive approach toward rehabilitation, which included a strict cardiac rehabilitation program, dietary adjustments, and a commitment to regular exercise. Within a year, not only did Alex return to his daily activities, but he also ran his first half-marathon, symbolizing his triumph over heart disease.
Challenges and How They Were Overcome
Yet, the path to recovery post-open heart surgery can be fraught with challenges. John, a congenital heart defect patient, faced several complications post-surgery, including infections and arrhythmias. What made John’s story remarkable was his survival and how he turned his challenges into an advocacy platform for heart health, emphasizing the importance of early detection and continuous care.
Emma’s recovery journey underscores the mental and emotional challenges patients often encounter. After her surgery, Emma battled depression and anxiety, common yet less discussed aspects of post-operative recovery. Through counseling, support groups, and mindfulness practices, Emma gradually found her footing, highlighting the critical need for comprehensive care that includes mental health support.
The Future of Open Heart Surgery
Research and Development
The future of open heart surgery looks promising. Research and development are focused on enhancing surgical techniques, reducing patient recovery time, and improving overall outcomes. Innovations such as minimally invasive surgical approaches, robotic-assisted surgeries, and developing more durable and biocompatible heart valves are at the forefront of transforming cardiac care.
Emerging Trends in Cardiac Care
Emerging trends in cardiac care emphasize a holistic and patient-centered approach, integrating technological advancements with a focus on preventive care and rehabilitation. Telemedicine and remote monitoring have become increasingly important, allowing for continuous patient care and early detection of potential complications.
FAQ on Open Heart Surgery
Q: What is open heart surgery?
A: Open heart surgery involves opening the chest and performing surgery on the heart’s muscles, valves, or arteries.
Q: How long does recovery from open heart surgery take?
A: Recovery can vary but typically ranges from 6 to 8 weeks. Full recovery, including a return to normal activities, may take several months.
Q: What are the risks of open heart surgery?
A: Risks include infection, bleeding, stroke, heart attack, and complications from anesthesia, though these risks are minimized with modern surgical techniques and post-operative care.
Q: How can I improve my chances of a successful outcome?
A: Follow your healthcare provider’s advice closely, according to the Journal of the American Medical Association. This includes taking medications as prescribed, attending all follow-up appointments, participating in cardiac rehabilitation, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Q: Is open heart surgery painful?
A: Patients are under anesthesia during surgery and feel no pain. Post-surgery, pain, and discomfort are managed with medications.
Q: Can I live a normal life after open heart surgery?
A: Many patients return to normal activities after recovery, though some lifestyle adjustments related to diet, exercise, and medication may be necessary.
3 thoughts on “Open Heart Surgery Survival Rate by Age”