Introduction of Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE)
Definition and Overview
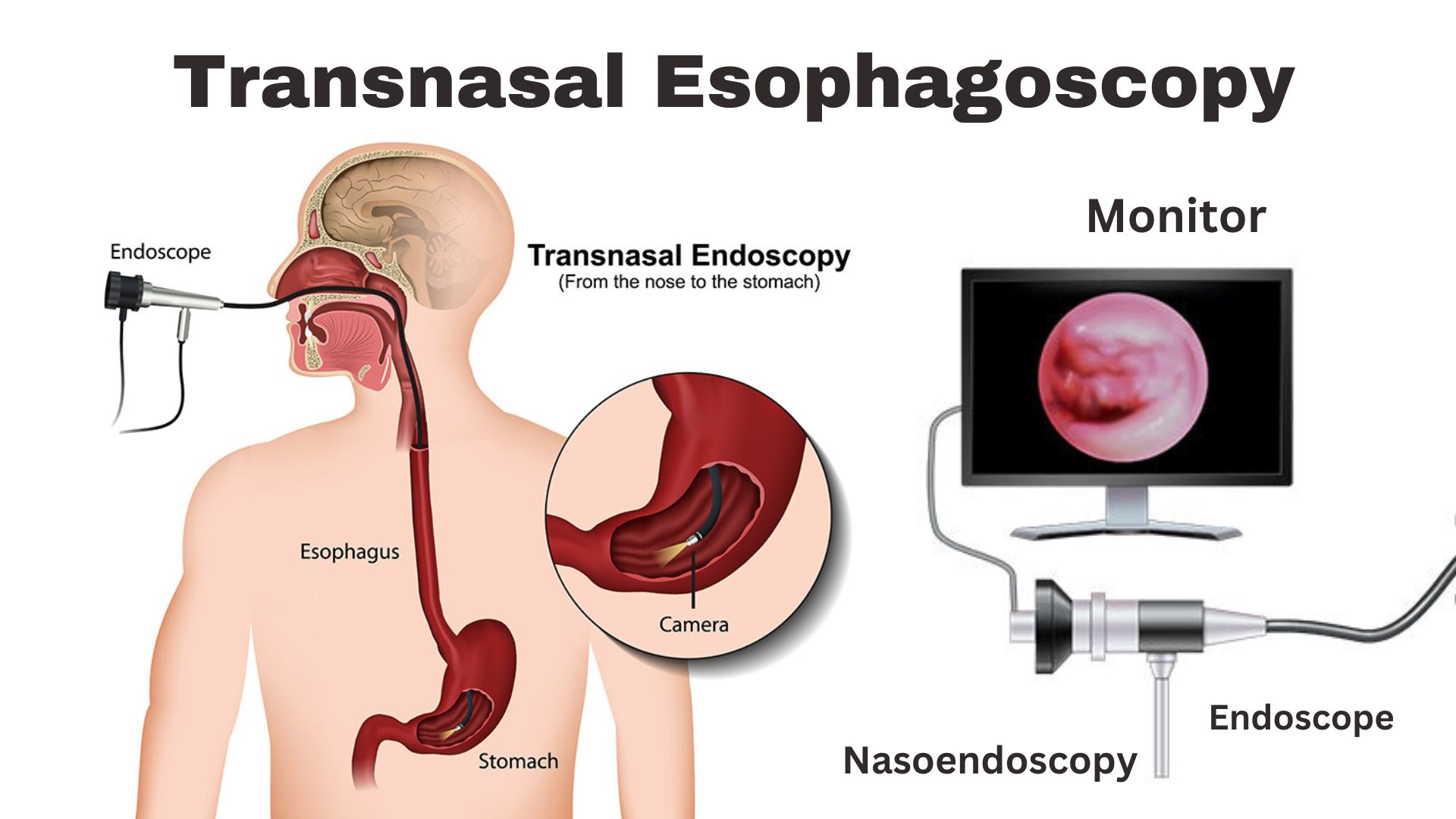
Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE) is a scientific method used to observe the inner lining of the esophagus between nose and throat, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. Unlike conventional esophagoscopy, which involves passing an endoscope through the mouth, TNE includes a skinny, flexible endoscope inserted via the nostril. This approach is less invasive, regularly more snug for the affected person, and does now not require fashionable anesthesia. It permits docs to diagnose and, once in a while, deal with conditions along with acid reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus, and esophageal cancer at an early stage.
Historical Background
The improvement of transnasal esophagoscopy marks a good advancement in gastroenterology and endoscopy. Initially, esophagoscopy was done with rigid scopes and required sedation or popular anesthesia, making the method more bulky and with higher dangers. The advent of flexible endoscopes in the latter half of the 20th century opened the door for more excellent patient-friendly strategies. Transnasal Esophagoscopy, emerging as a polished technique in the early twenty-first century, capitalized on miniaturization and imaging technology improvements to provide a much less invasive, properly tolerated option for patients.
Importance in Modern Medicine
In modern medicine, TNE is vital in the early detection and management of esophageal illnesses. Its minimum invasiveness permits techniques to be performed in an outpatient setting, decreasing healthcare expenses and improving patient comfort. Additionally, the convenience of use and affected person consolation associated with TNE encourages earlier and more common screenings, doubtlessly primary to higher consequences for patients with chronic esophageal conditions.
How Transnasal Esophagoscopy Works
Pre-Procedure Preparations
Before undergoing TNE, sufferers are usually advised to fast for a short duration, generally 6 to 8 hours, to ensure the esophagus is visible. Detailed clinical records and modern medications are reviewed to reduce capability dangers. Since the system is minimally invasive, the need for pre-process medicines is decreased; however, a nearby anesthetic might be applied to the nasal passages to ease the insertion of the endoscope.
The Procedure Step-by-Step
Transnasal Esophageoscopy represents a leap forward in diagnostic abilities, combining patient comfort with effective ailment control. Its role in current medication continues to develop as advancements in generation and technique make it an increasingly treasured device for the early detection and remedy of esophageal conditions.
- Anesthetic Application: A nearby anesthetic is carried out to the affected person’s nasal passage to numb the area and reduce pain.
- Scope Insertion: A skinny, flexible endoscope is gently inserted through one nose. The affected person can breathe generally at some point during this time.
- Examination: The health practitioner cautiously advances the endoscope down the nasal passage, through the throat, and into the esophagus. Real-time pictures are transmitted to a display screen, allowing an in-depth exam of the esophagus and stomach lining.
- Biopsies or Treatments: If vital, tiny devices can be passed through the endoscope to take tissue samples (biopsies) or carry out minor remedies.
What Happens After the Procedure
Following TNE, sufferers can resume regular sports immediately, with few regulations. They may enjoy a slight sore throat or soreness in the nose. However, those signs typically subside within a few hours. Results from the exam are regularly discussed quickly after the procedure, even though globus effects can also take longer. Patients are recommended to follow up with their medical doctor for further remedy or tracking, primarily based on the findings of the TNE.
Applications Anesthesia and Benefits of TNE
Diagnosing Esophageal Diseases
Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE) is a pivotal device in the early detection and evaluation of esophageal illnesses. This minimally invasive method allows a proper-away view of the dysphagia, assisting in discovering conditions that include Barrett’s esophagus, maximum esophageal cancers, eosinophilic esophagitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Early detection through TNE can substantially enhance treatment outcomes and patient prognosis by allowing nicely-timed intervention.
Monitoring Conditions Over Time
TNE is valuable for initial evaluation and crucial in tracking esophageal situations’ progression. For patients with persistent esophageal illnesses, ordinary TNE techniques can help doctors investigate the effectiveness of remedies, alter remedy plans as wished, and come across any signs of worsening or improvement. This ongoing monitoring is essential for managing prolonged periods of health and preventing complications.
Advantages Of Traditional Esophagoscopy
TNE offers numerous advantages over traditional esophagoscopy techniques:
- Minimally Invasive: TNE is finished through the nasal passage, addressing the want for sedation and the associated risks. This approach is much less invasive, decreasing the affected person’s pain and restoration time.
- Cost-Effective: The method is frequently more fee-effective than conventional esophagoscopy, partially because it can be finished in an outpatient setting without well-known anesthesia.
- Patient Convenience: Since no sedation is wanted, sufferers can commonly resume their regular sports rapidly after the system, making it an available preference for humans with busy schedules.
Safety: Compared to traditional techniques, the risk of complications, which incorporates infections or poor reactions to anesthesia, is notably decreased with TNE.
Potential risks of transnasal esophagoscopy and Complications
Common Side Effects
Although TNE is considered secure and nicely tolerated, a few commonplace thing outcomes may additionally moreover get up, which include:
- Nasal Discomfort: Some patients experience minor pain or irritation in the nasal passage during or after the device.
- Throat Irritation: The endoscope passage can temporarily cause sore throat or soreness.
Nosebleed: A minor nosebleed is possible but typically resolves quickly.
Rare, however, Serious Risks
Transnasal Esophagoscopy vital complications can arise, together with perforation of the esophagus or severe bleeding, mainly if biopsies are taken. Infections are other uncommon but possible hazards.
While uncommon, there are a few severe risks related to TNE:
- Esophageal Perforation: An unusual, severe hardship with a tear within the esophagus wall. This situation calls for an instant scientific hobby.
- Infection: Although rare, there is a moderate chance of contamination because of the stringent sterilization protocols accompanied by the system.
How Risks Are Minimized
Healthcare groups take several steps to limit the risks associated with TNE:
- Thorough Patient Screening: Patients are carefully screened to ensure they may be appropriate candidates for TNE, considering their scientific statistics and modern-day fitness situations.
- Use of Sterile Equipment: All gadgets used sooner or later in TNE are sterilized to prevent infections.
- Skilled Practitioners: The technique is completed by experienced professionals trained in TNE who ensure it is performed safely and correctly.
- Pre-Procedure Preparations: Patients are given particular commands on how to put together the system, including any nutritional rules, to reduce the danger of complications.
- Post-Procedure Care: After TNE, sufferers acquire suggestions on managing any pain and are advised to report any uncommon signs without delay.
Patient Experience and Recovery Prepare for Transnasal Esophagoscopy
What Patients Can Expect
Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE) is a less invasive method for inspecting the esophagus, making the affected person’s experience extraordinarily comfortable compared to standard esophagoscopy approaches. Patients undergoing TNE can expect minimum pain because the flexible scope is inserted through the nostril, bypassing the need to skip via the throat immediately, frequently reducing gagging and discomfort. Local anesthesia is generally finished inside the shape of a nasal spray to numb the nasal passages and decrease any ability pain. During the technique, patients are wakeful and have respiration; generally, that’s a consolation for the masses, as ultra-modern anesthesia isn’t required.
Recovery Time and Tips
Healing from Transnasal Esophagoscopy is substantially speedy. Most patients can resume their normal sports activities and food regimen immediately after the technique, barring any specific instructions from their healthcare provider. Some may additionally experience minor throat discomfort or a stuffy nose, but these signs and symptoms are commonly solved within a few hours. Also, visit my Other post, Open Heart Surgery Survival Rate by Age.
Recovery tips include:
- Drinking hundreds of water to help soothe the throat.
- Avoid warm or tremendously spiced meals immediately after the method if the throat feels slightly sore.
- Use a saline nasal spray to alleviate any nasal ache if encouraged by the doctor.
Patients are usually counseled to look for any unusual symptoms and report them to their healthcare provider if they experience incredible aches, bleeding, or other concerning symptoms, even though those are uncommon.
Patient Testimonials
Patient stories with TNE regularly spotlight the benefits of the technique. Many precise surprises on the minimal soreness skilled and the short return to regular activities. For example, one affected man or woman mentioned, “I became apprehensive about having something inserted through my nose, but the actual manner became much less difficult than I predicted. I had a moderate sore throat, but it disappeared after some hours. I might also want to eat and go about my day normally.”
Final Thoughts Swallow on TNE
The Future of Transnasal Esophagoscopy
Transnasal Esophagoscopy appears promising, with ongoing improvements to enhance the method’s diagnostic talents, affected person comfort, and accessibility. Innovations in the imaging era and improving even thinner, more flexible scopes can permit even less invasive methods and more precise views of the esophagus. As studies keep, TNE may discover broader programs, including more sophisticated diagnostic and therapeutic uses.
Encouragement for Further Discussion and Consultation
Transnasal Esophagoscopy offers a much less invasive, efficient alternative to conventional techniques for people experiencing symptoms that might warrant a closer study of the esophagus or for those wanting recurring tracking for present situations. Sufferers need to discuss their alternatives with their healthcare companies, who can offer customized recommendations primarily based on a person’s fitness wishes and conditions. The simplicity and simplicity of TNE could make it the precise desire for plenty, potentially improving the prognosis and monitoring of esophageal conditions with minimum affected individual aches.
Frequently Asked Questions about Transnasal Esophagoscopy
1. What is Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE)?
TNE is a minimally invasive system used to examine the esophagus’s liner. It involves passing a skinny, flexible endoscope through the nostril, requiring no sedation and minimal preparation. Thus, it is a quick and comfortable choice for sufferers.
2. Is the Transnasal Esophagoscopy procedure painful?
Most patients revel in minimal discomfort throughout TNE. Local anesthesia numbs the nasal passages, decreasing sensation and pain. Patients can also sense stress or a moderate tickling sensation, but there is commonly no ache.
3. How long does a TNE method take?
The actual TNE system is extraordinarily brief, usually taking approximately five to ten minutes to complete. However, guidance and restoration time might also take a couple of minutes to the general go-to.
4. Can I devour it earlier than a transnasal esophagoscopy?
In most cases, patients are cautioned to avoid eating or ingesting for a short period before the procedure, generally approximately 4 to 6 hours, to ensure a clear view of the esophagus. Your healthcare provider will develop precise commands based totally on your scenario.
5. How soon will I get the consequences from my TNE?
Initial observations can frequently be shared with you right away after the system. However, if biopsies are taken, those samples will want to be analyzed in a lab, which may take some days to a week.
Conclusion
Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE) marks a giant development in gastrointestinal diagnostics, imparting a less invasive, more patient-pleasant alternative to standard esophagoscopy techniques. By minimizing pain and eliminating the need for sedation, Transnasal Esophagoscopy is no longer the most effective, making the manner extra accessible and less daunting for patients; additionally, it enables faster restoration, allowing for an instantaneous go back to everyday activities. As era and medical practices continue to adapt, TNE stands out as a testimony to the continued upgrades in patient care, emphasizing efficiency, comfort, and the significance of early and accurate analysis in the control of esophageal situations.
1 thought on “Transnasal Esophagoscopy Enhances Early Diagnosis: 5 Benefits in 2024”