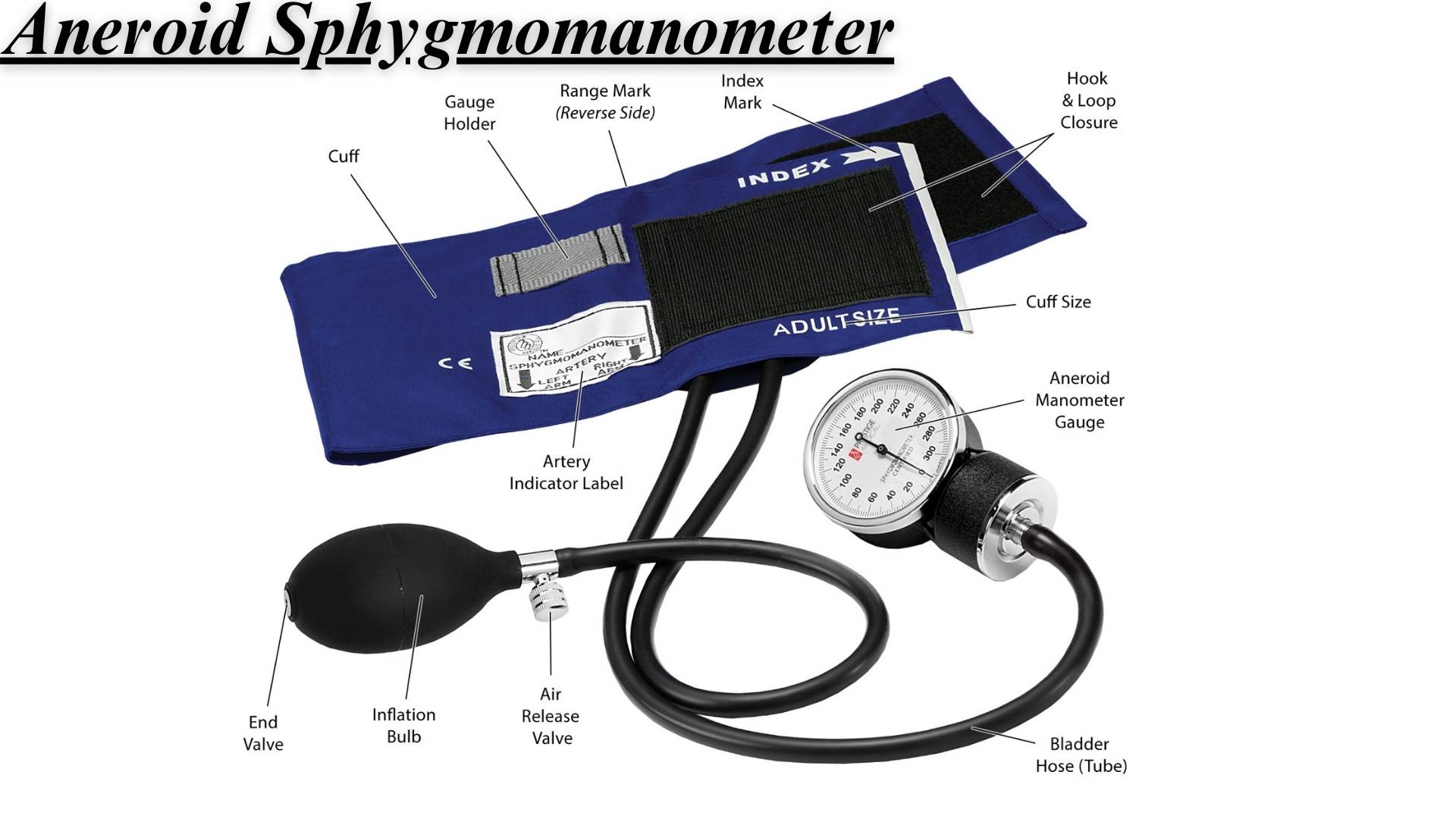
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer
Overview
An aneroid sphygmomanometer is a medical device used to measure blood pressure without mercury. This instrument is vital for healthcare professionals and individuals who monitor blood pressure regularly. It comprises a cuff designed to compress the arm, a pump to inflate the cuff, and a mechanical gauge to read the pressure. Unlike digital monitors, aneroid devices offer mechanical precision, which is crucial in many medical settings.
History and Development
The aneroid sphygmomanometer was developed as an alternative to the mercury sphygmomanometer due to safety concerns with handling toxic mercury. The first practical aneroid sphygmomanometer was introduced in the early 20th century. Over the years, improvements have been made to enhance the accuracy, durability, and usability of these devices. Their widespread adoption in clinics worldwide reflects their reliability and the trust medical professionals place in them.
Key Components
The key components of an aneroid sphygmomanometer include:
- Cuff: Wraps around the patient’s arm and is inflated to restrict blood flow.
- Pressure Gauge: Displays the blood pressure reading calibrated in millimetres of mercury (mmHg).
- Bulb: Used for inflating the cuff manually.
- Valve: Allows for controlled deflation of the cuff for accurate measurement. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the accurate measurement of blood pressure.
How an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer Works
The Mechanism
The mechanism of an aneroid sphygmomanometer involves the mechanical linkage between the cuff and a dial gauge. As the cuff inflates, it compresses the artery under the cuff to a point where no blood flows (systolic pressure) and then gradually deflates. During deflation, the gauge measures the pressures at which blood flow starts (systolic) and when it returns to normal (diastolic).
Measuring Blood Pressure
To measure blood pressure, the cuff is placed around the upper arm and inflated to a pressure higher than the patient’s expected systolic pressure. As the air is slowly released, a stethoscope is used to listen to the sounds of the blood flow in the artery. The first sound heard represents the systolic pressure, and the point at which the sound disappears represents the diastolic pressure. These sounds are known as Korotkoff sounds.
Importance of Calibration
Calibration is crucial for ensuring that an aneroid sphygmomanometer provides accurate readings. Over time, the mechanical components can wear or get misaligned, leading to incorrect blood pressure readings. Regular calibration, recommended at least annually, involves comparing the device’s readings with those of a standard, usually a calibrated mercury sphygmomanometer, and making adjustments if necessary. Calibration ensures the device remains reliable and safe for diagnosing and monitoring hypertension and other health conditions.
Benefits of Using an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer

Accuracy
When used correctly, an aneroid sphygmomanometer provides highly accurate readings. This type of device measures blood pressure mechanically without relying on digital algorithms, which can sometimes lead to discrepancies. Healthcare professionals often prefer aneroid devices for their precision, particularly in clinical settings where accurate measurements are crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions like hypertension.
Durability
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are known for their robust construction. The lack of electronic components makes them less susceptible to damage caused by drops or electrical failures. Their mechanical nature ensures that they can last for many years with proper maintenance, making them a cost-effective option for both medical professionals and home users.
Ease of Use
While aneroid sphygmomanometers require a bit of practice to master, they are straightforward to use once the technique is learned. They typically involve a manual pump and a gauge, which provides a direct and clear readout of blood pressure levels. This simplicity makes it easier for users to operate the device without the need for extensive training or familiarity with digital technology.
Comparison with Digital Blood Pressure Monitors

Accuracy and Reliability
Digital blood pressure monitors are popular for their convenience, but they can sometimes offer variable results, especially if not positioned correctly. Aneroid devices, on the other hand, tend to provide more consistent and reliable readings when used properly. The manual measurement process allows for less deviation and can be more trustworthy in critical care situations.
Ease of Use
Digital monitors are generally easier to use compared to aneroid types. They often come with automatic features such as inflation, deflation, and digital readouts, making them user-friendly, especially for individuals who find manual operations challenging. This convenience can be particularly beneficial for home users or for those who require frequent monitoring.
Cost Considerations
Digital blood pressure monitors can vary widely in cost. Basic models may be comparable in price to aneroid devices, but more advanced digital models with additional features like Bluetooth connectivity or data logging capabilities can be significantly more expensive. Aneroid sphygmomanometers typically offer a lower long-term cost due to their durability and lack of electronic components, which may need fewer replacements over time.
How to Properly Use an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer

Correct Placement of the Cuff
The placement of the cuff is critical to ensure accurate blood pressure readings. The cuff should be wrapped around the upper arm at about the level of the heart. It should be snug but not too tight, with enough space to slide two fingertips under the top edge of the cuff. The lower edge of the cuff should be about an inch above the elbow crease. Ensuring the cuff is neither too loose nor too tight is vital for accurate measurement.
Inflation and Deflation Process
Once the cuff is properly placed, use the bulb to inflate the cuff gradually. Inflate the cuff until the gauge reads about 20-30 mmHg higher than the expected systolic pressure. Begin to slowly deflate the cuff using the valve, ideally at a rate of about 2-3 mmHg per second. This controlled deflation is crucial for accurate readings.
Reading the Measurements
As you deflate the cuff, listen with a stethoscope placed over the brachial artery just below the cuff’s edge or watch the gauge. The point at which you first hear a thumping sound is the systolic pressure. The point where this thumping sound completely disappears represents the diastolic pressure. Read the gauge precisely at these points to determine the blood pressure values.
Maintaining Your Aneroid Sphygmomanometer
Cleaning and Storage
Keep the sphygmomanometer clean by wiping the cuff and dial with a damp cloth, avoiding harsh chemicals that could damage the materials. Ensure the device is completely dry before storing it. Store the sphygmomanometer in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent the rubber components from deteriorating.
Regular Calibration
Aneroid sphygmomanometers should be calibrated at least once a year to ensure accuracy. If the sphygmomanometer is used frequently, more regular checks might be necessary. Calibration involves checking the readings from the aneroid device against a standard mercury sphygmomanometer and adjusting it if discrepancies are found.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with aneroid sphygmomanometers include needle sticking, inaccurate readings, or difficulty pumping the cuff. If the needle sticks, it might need to be recalibrated or replaced. If readings are consistently off, verify the technique first, then check for air leaks in the cuff or tubing. For issues with inflation, ensure the bulb and valves are not leaking air and replace them if necessary.
Choosing the Right Aneroid Sphygmomanometer
Factors to Consider
When selecting an aneroid sphygmomanometer, several factors need to be considered to ensure you get a reliable and efficient device. Firstly, assess the cuff size, which should match the arm circumference of the person who will use it most frequently. Secondly, look for a gauge that is easy to read and well-calibrated. The durability of the materials and the reputation of the manufacturer are also crucial. Additionally, consider if the model includes a stethoscope or if it needs to be purchased separately.
Recommended Brands
Several reputable brands are recognized for producing high-quality aneroid sphygmomanometers. Brands like ADC, Welch Allyn, and MDF Instruments are well-regarded in the medical community for their accuracy and durability. These companies offer various models that cater to different professional needs and personal preferences.
Price Range
The price of an aneroid sphygmomanometer can vary widely based on the brand, features, and quality. Basic models suitable for home use might start around $20-$30, while high-end models designed for clinical settings can cost upwards of $100. Investing in a higher-priced model might be worthwhile for medical professionals due to the higher quality and better durability.
Common Misconceptions and Errors

Misconceptions About Accuracy
A common misconception is that aneroid sphygmomanometers are inherently less accurate than digital models. However, when properly calibrated and used, they can provide highly accurate readings. The key is regular maintenance and understanding how to use the device correctly.
Common User Errors
User errors often include incorrect cuff placement, using a cuff of the wrong size, or reading the gauge improperly. Such mistakes can lead to inaccurate readings, which might affect medical assessments or treatment plans.
How to Avoid Mistakes
To avoid common errors, always ensure the cuff is placed on the bare upper arm at heart level. Use a cuff that fits properly, and educate yourself on reading the gauge accurately. Regular training sessions or refreshers can help maintain skills, especially in a professional healthcare setting.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer in Medical Practice

Usage in Clinical Settings
In clinical settings, aneroid sphygmomanometers are often preferred due to their reliability and precision. They are used in environments ranging from doctor’s offices to intensive care units, where accurate blood pressure measurement is critical.
Benefits for Healthcare Professionals
For healthcare professionals, the reliability of an aneroid sphygmomanometer allows for consistent patient monitoring. These devices do not rely on electricity, making them portable and functional in various settings, including during power outages or in remote areas.
- Enhanced diagnostic accuracy
- Improved patient outcomes
- Increased efficiency in care delivery
- Access to ongoing professional development and training
Case Studies and Applications
Case studies have shown the effectiveness of aneroid sphygmomanometers in managing conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, and other cardiovascular disorders. Real-world applications demonstrate their utility in emergency scenarios, medical camps, and regular patient assessments, showcasing their indispensable role in healthcare.
- Clinical Evaluation: Used in hospitals and clinics for routine blood pressure checks and monitoring patient vitals.
- Home Monitoring: Allows patients to manage hypertension or low blood pressure from home with reliable accuracy.
- Field Use in Remote Areas: This tool is essential for health workers in areas without electricity due to its portability and lack of batteries.
- Educational Purposes: Used in medical training and educational programs to teach students about blood pressure measurement techniques.